Difference between revisions of "Openshift - HAproxy metrics EN"
(→Collecting metrics from the access logs) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
:[[File:ClipCapIt-190807-102633.PNG]] | :[[File:ClipCapIt-190807-102633.PNG]] | ||
| Line 569: | Line 568: | ||
* '''port: 9144''' -> The http port of the /metrics endpoint | * '''port: 9144''' -> The http port of the /metrics endpoint | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | {{warning | | + | {{warning |Do not forget to set the value of '''readall''' to 'false' in a live environment as it can significantly degrade performance}} |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 630: | Line 629: | ||
CMD sh -c "nohup /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -i ${PID_DIR}/pid -n &" && ./grok_exporter -config /grok/config.yml | CMD sh -c "nohup /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -i ${PID_DIR}/pid -n &" && ./grok_exporter -config /grok/config.yml | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | {{note | It is important to use grok-exporter version 0.2.7 or higher, as functions were introduced in this version}} | + | {{note |It is important to use grok-exporter version 0.2.7 or higher, as functions were introduced in this version}} |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 745: | Line 744: | ||
cluster role "cluster-admin" added: "admin" | cluster role "cluster-admin" added: "admin" | ||
</Pre> | </Pre> | ||
| − | {{note | If we get this error '''Error from server (NotFound): the server could not find the requested resource''', it probably means that our oc client is older than OpenShift version}} | + | {{note|If we get this error '''Error from server (NotFound): the server could not find the requested resource''', it probably means that our oc client is older than OpenShift version}} |
| Line 926: | Line 925: | ||
- system: serviceaccount: default: haproxy-exporter | - system: serviceaccount: default: haproxy-exporter | ||
... | ... | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| Line 1,017: | Line 1,016: | ||
deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated | deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | {{note | In minishift, in the router containers the name resolution does not work for Kubernetes service names, because it doesn't use the Kubernetes cluster DNS server but the minishfit VM. Therefore, all you have to do is enter the service's IP address instead of its name. In OpenShift, we have to use the name of the service}} | + | {{note|In minishift, in the router containers the name resolution does not work for Kubernetes service names, because it doesn't use the Kubernetes cluster DNS server but the minishfit VM. Therefore, all you have to do is enter the service's IP address instead of its name. In OpenShift, we have to use the name of the service}} |
As a second step, change the HAproxy log level to debug, because it only produces access log in debug level. | As a second step, change the HAproxy log level to debug, because it only produces access log in debug level. | ||
| Line 1,024: | Line 1,023: | ||
deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated | deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | {{warning | Performance test must be carried out to see how much is the extra load when running the haproxy in debug mode}} | + | {{warning|Performance test must be carried out to see how much is the extra load when running the haproxy in debug mode}} |
| Line 1,080: | Line 1,079: | ||
Please open the gork-exporter metrics at http://<pod IP>:9144/metrics. You can open this URL either in the haproxy-exporter pod itself with on localhost or in any other pod using the haporxy-exporter pod's IP address. We have to see the '''haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket''' histogram among the metrics. | Please open the gork-exporter metrics at http://<pod IP>:9144/metrics. You can open this URL either in the haproxy-exporter pod itself with on localhost or in any other pod using the haporxy-exporter pod's IP address. We have to see the '''haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket''' histogram among the metrics. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | # kubectl exec -it test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8 / bin / bash -n mynamespace | + | # kubectl exec -it test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8/bin/bash -n mynamespace |
$ | $ | ||
$ curl http://172.30.213.183:9144/metrics | $ curl http://172.30.213.183:9144/metrics | ||
| Line 1,114: | Line 1,113: | ||
static_configs: | static_configs: | ||
- targets: ['grok-exporter-service.default: 9144'] | - targets: ['grok-exporter-service.default: 9144'] | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| − | |||
=== Pod Level Data Collection === | === Pod Level Data Collection === | ||
| Line 1,241: | Line 1,239: | ||
= OpenShift router + rsyslog = | = OpenShift router + rsyslog = | ||
| − | Starting with OpenShift 3.11, it is possible to | + | Starting with OpenShift 3.11, it is possible to fire up a router that will contain a side car rsyslog container in the router pod and configure HAproxy to send logs to the rsyslog server via an emptyDir volume , which writes them to stdout by default. The configuration of rsyslog is in a configMap. |
[[File: ClipCapIt-190810-164907.PNG]] | [[File: ClipCapIt-190810-164907.PNG]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | You can create a router with syslogserver using the '''--extended-logging''' switch | + | You can create a router with syslogserver using the '''--extended-logging''' switch in the '''' 'oc adm router''' command. |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# oc adm router myrouter --extended-logging -n default | # oc adm router myrouter --extended-logging -n default | ||
| Line 1,261: | Line 1,259: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Turn on | + | Turn on debug level loging in HAproxy: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# oc set env dc / myrouter ROUTER_LOG_LEVEL = debug -n default | # oc set env dc / myrouter ROUTER_LOG_LEVEL = debug -n default | ||
| Line 1,297: | Line 1,295: | ||
| − | You can see that the '''/ var / lib / rsyslog /''' folder is mounted in both containers. | + | You can see that the '''/var/lib/rsyslog/''' folder is mounted in both containers. The rsyslog.sock file will be created here. |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== router container === | === router container === | ||
| − | When we enter the router container, we can see that the configuration has already been | + | When we enter the router container, we can see that the configuration has already been modified: |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# kubectl exec -it myrouter-2-bps5v / bin / bash -n default -c router | # kubectl exec -it myrouter-2-bps5v / bin / bash -n default -c router | ||
| Line 1,333: | Line 1,331: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | If you want to reconfigure rsyslog to send logs to | + | If you want to reconfigure rsyslog to send logs to e.g, logstash then you only need to rewrite the configMap. By default, rsyslog only writes to stdout. |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
# kubectl get cm rsyslog-config -n default -o yaml | # kubectl get cm rsyslog-config -n default -o yaml | ||
Latest revision as of 10:42, 25 January 2020
Contents
- 1 Preliminary
- 2 Using HAproxy Metric Endpoint
- 3 Collecting metrics from the access logs
- 4 OpenShift router + rsyslog
Preliminary
Overview
In OpenShift 3.11, the default router is the HAProxy template router. This is based on the of the 'openshift3 / ose-haproxy-router' image. The image runs two components inside a container, one is HAproxy itself and the other is the router controller, the tempalte-router-plugin, which maintains the HAproxy configuration. The router POD listens on the host machine's network interface and directs external requests to the appropriate pod within the OpenShfit cluster. Unlike Kubernetes Ingress, OS routers do not have to run on all nodes, they are installed just on dedicated nodes, so external traffic must be directed to the public IP address of these nodes.
HAProxy provides standard prometheus metrics through the router's Kubernetes service. The problem is that only a very small part of the metrics provided by HAproxy can be used meaningfully. Unfortunately, the http response-time metric is calculated from the average of the last 1024 requests, making it completely unsuitable for real-time monitoring purposes.
Real requests and responses information is only provided in the HAProxy acces-log, and only in debug mode, but it is really detailed, it contains all parameters of the requests / responses. These logs can be used to generate prometheus metrics using multiple tools (e.g. grok-exporter, Fluentd, Logstash).
Haproxy main configuration
The HAproxy configuration file is located in '/var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config'. It contains all the services that are configured in the router.
/var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config
global ... log 127.0.0.1 local1 debug backend config: ##-------------- app level backends ---------------- .... backend be_edge_http:mynamespace:test-app-service mode http ... server pod:test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8:test-app-service:172.17.0.12:8080 172.17.0.12:8080 cookie babb614345c3670472f80ce0105a11b0 weight 256
The backends that belong to the route are listed in the app level backends section. You can see in the example that the backend called test-app-service is available at 172.17.0.12:8080.
Git repository
All the required resources used in the following implementation are available in the following git repository: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics
Http test application
For generating http traffic, I made a test application that can generate different response time and http response codes. Source available here: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics/tree/master/test-app
The Kubernetes install files can be found at the root of the git repository.
After installation use the application based on the following:
- http://test-app-service-mynamespace.192.168.42.185.nip.io/test/slowresponse/ <delay in millisecundum>
- http://test-app-service-mynamespace.192.168.42.185.nip.io/test/slowresponse/ <delay in milliseconds> / <http response code>
Using HAproxy Metric Endpoint
HAproxy has a built-in metric endpoint, which by default provides Prometheus metrics, but most of its metrics are not really usable. There are two metric types that are worth mentioning. One of them counts the responses with 200 http code, and the other counts the responses with 500 (bad request).
The metric endpoint (/metrics) is turned on by default. This can be turned off, but HAProxy will still collect metrics in the background. The HAproxy pod is made up of two components. One is HAproxy itself and the other is the router-controller that manages the HAproxy configuration. Metrics are collected from both components every 5 seconds by the metric manager. Frontend and backend metrics are both collected, grouped by services.
Query Metrics
There are two ways to query metrics.
- Basic authentication with username + password: /metrics http endpoint
- Authentication with Kubernetes RBAC Rules: For machine processing (e.g. in Prometheus) it is possible to enable RBAC rule based authentication for a given service-account.
User + password based authentication
The default metrics URL is:
http://<user>:<password>@<router_IP>:<STATS_PORT>/metrics
The user, password, and port can be found in the in the service definition for the HAproxy router.
# kubectl get svc -n default NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE router ClusterIP 172.30.130.191 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,1936/TCP 4d
You can see that there is an extra port listed upon the default 80 and 433, which is the 1936,that is the port of the metrics endpoint.
Now, let's examine the definition of the service to extract the username and password:
# kubectl get svc router -n default -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.openshift.io/password: 4v9a7ucfMi
prometheus.openshift.io/username: admin
...
According to this, the URL of the metrics endpoint using the node's IP address (minishfit IP in the example) is the following: http://admin:4v9a7ucfMi@192.168.42.64:1936/metrics (You can't invoke this URL in web-browsers as they aren't familiar with this format, use curl for testing it in the command line)
# curl admin:4v9a7ucfMi@192.168.42.64:1936/metrics
# HELP apiserver_audit_event_total Counter of audit events generated and sent to the audit backend.
# TYPE apiserver_audit_event_total counter
apiserver_audit_event_total 0
# HELP apiserver_client_certificate_expiration_seconds Distribution of the remaining lifetime on the certificate used to authenticate a request.
# TYPE apiserver_client_certificate_expiration_seconds histogram
apiserver_client_certificate_expiration_seconds_bucket{le="0"} 0
apiserver_client_certificate_expiration_seconds_bucket{le="21600"} 0
...
ServiceAccount based authentication
It is possible to query the HAproxy metrics not only with basic authentication, but also with RBAC rules.
We need to create a ClusterRole that allows the Prometheus service-account to query the routers/metrics endpoint.
cr-prometheus-server-route.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
component: server
release: prometheus
name: prometheus-server-route
rules:
- apiGroups:
- route.openshift.io
resources:
- routers/metrics
verbs:
- get
The second step is to create a ClusterRoleBinding that binds the Prometheus serviceAccount with the new role.
crb-prometheus-server-route.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
chart: prometheus-8.14.0
component: server
release: prometheus
name: prometheus-server-route
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: prometheus-server-route
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: prometheus-server
namespace: mynamespace
Let's create the two new objects:
# kubectl apply -f cr-prometheus-server-route.yaml clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus-server-route created # kubectl apply -f crb-prometheus-server-route.yaml clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus-server-route created
Prometheus integration
Lets examine the Endpoint definition of the HAproxy router. Based on that, we can create the Prometheus configuration that will be responsible for finding runtime all the pods running HAproxy instances. We have to find the OpenShift endpoint object with the name router that have a port definition called 1936-tcp. Prometheus will extract the port number for the metrics query form this port-definition (/metrics).
# kubectl get Endpoints router -n default -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2019-07-09T20:26:25Z"
labels:
router: router
name: router
subsets:
ports:
- name: 1936-tcp
In the Promethues configuration, you need to add a new target with kubernetes_sd_configs that will look for endpoints with the name router and with the port 1936-tcp.
- job_name: 'openshift-router'
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/service-ca.crt
server_name: router.default.svc
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/scraper/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
namespaces:
names:
- default
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
action: keep
regex: router;1936-tcp
Update the ' 'ConfigMap of your Prometheus configuration.
# kubectl apply -f cm-prometheus-server-haproxy.yaml configmap/prometheus-server created
Let's look into the logs of the side card container running in the Promethues pod (responsible for reloading the configuration).
# kubectl logs -c prometheus-server-configmap-reload prometheus-server-75c9d576c9-gjlcr -n mynamespace 2019/07/22 19:49:40 Watching directory: "/etc/config" 2019/07/22 20:25:36 config map updated 2019/07/22 20:25:36 successfully triggered reload
Lets check the Prometheus logs as well:
# kubectl logs -c prometheus-server prometheus-server-75c9d576c9-gjlcr -n mynamespace ... level = info ts = 2019-07-22T20: 25: 36.016Z caller = main.go: 730 msg = "Loading configuration file" filename = / etc / config / prometheus.yml
Next, open the Promethues console and navigate to the 'target' page: http://mon.192.168.42.185.nip.io/targets
If there were more routers in the cluster, they would be all listed as separate endpoints.
Metric types
At first glance, there are two meaningful metrics provided by the HAproxy. These are the following:
haproxy_server_http_responses_total
It is a Prometheus counter, shows how many 200 and 500 http replies a given service gave per backend. It is on service level only. Unfortunately, we do not receive information on http 300 and 400 errors. We will also get these from the access log
Let's generate a 200 answer using the test application. We need to see the counter of the 200 responses grows by one: http://test-app-service-mynamespace.192.168.42.185.nip.io/test/slowresponse/1/200
haproxy_server_http_responses_total {code = "2xx", Job = "openshift router" namespace = "mynamespace" pod = "body-app", route = "body-app-service" service = "body-app-service"} 1
Let's generate a 500 response using the test application again. This time, the counter of the 500 responses grows by one: http://test-app-service-mynamespace.192.168.42.185.nip.io/test/slowresponse/1/500
haproxy_server_http_responses_total {code = "5xx" job = "openshift router" namespace = "mynamespace" pod = "body-app", route = "body-app-service" service = "body-app-service"} 1
haproxy_server_response_errors_total
Counter type
haproxy_server_response_errors_total{instance="192.168.122.223:1936",job="openshift-router",namespace="mynamespace",pod="test-app-57574c8466-pvcsg",route="test-app-service",server="172.17.0.17:8080",service="test-app-service"}
Collecting metrics from the access logs
Overview
The task is to process the access log of HAproxy with a log parser and generate Prometheus metrics that are available for Prometheus through an HTTP endpoint. We will use the grok-exporter tool, which can do both. It can read logs from a file or stdin and generate metrics based on the logs. The grok-exporter will receive the logs from HAproxy via an rsyslog server. Rsyslog will put logs into file from which grok-exporter will be able to read them. Grok-exporter converts logs into promethues metrics.
Necessary steps:
- We have to create a docker image from grok-exporter that has rsyslog in the image. (The container must be able to run the rsyslog server as root, which requires extra openShfit configuration)
- The grok-exporter configuration will be in OpenShfit ConfigMap and the rsyslog workspace must be an OpenShift volume (writing a containers file system in runtime is really inefficient)
- We have to create a ClasterIP-type service that can perform load-balancing between grok-exporter pods.
- The HAproxy routers should be configured to write access logs in debug mode and send them to the remote rsyslog server running next to the grok-exporter.
- The rsyslog server running in the grok-exporter pod will both write the received logs into file (/var/log/messages - emptyDir type volume) and sends them to stdout as well for central log processing.
- Logs written to stdout will be picked up by the docker-log-driver and forwarded to the centralized log architecture (log retention)
- The grok-exporter program reads /var/log/messages and generates Prometheus metrics from the HAproxy access-logs.
- The Prometheus scrape config has to be extended with a kubernetes_sd_configs section. Prometheus must collect the metrics directly from the grok-exporter pods, not through the Kubernetes service to bypass load-balancing
HAproxy log structure
https://www.haproxy.com/blog/introduction-to-haproxy-logging/
HAproxy provides the following log structure for each request-response pair:
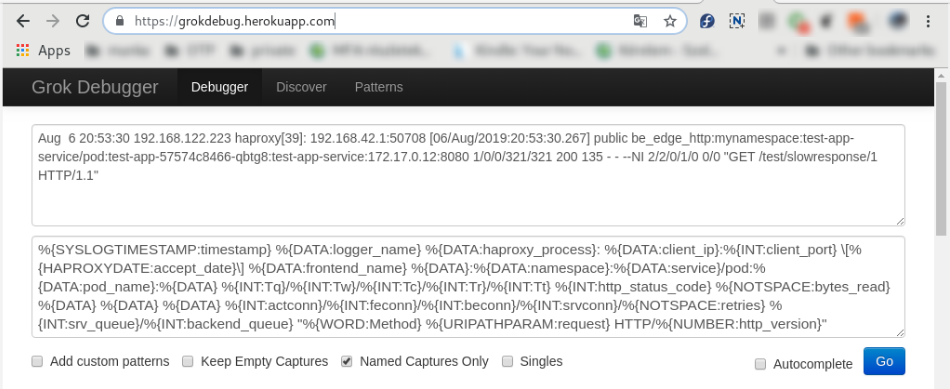
Aug 6 20:53:30 192.168.122.223 haproxy[39]: 192.168.42.1:50708 [06/Aug/2019:20:53:30.267] public be_edge_http:mynamespace:test-app-service/pod:test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8:test-app-service:172.17.0.12:8080 1/0/0/321/321 200 135 - - --NI 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET /test/slowresponse/1 HTTP/1.1"
Field Format Extract from the example above
1 Log writing date: Aug 6 20:53:30
2 HAproxy instant name: 192.168.122.223
3 process_name '[' pid ']:' haproxy[39]:
4 client_ip ':' client_port 192.168.42.1:50708
5 '[' request_date ']' [06/Aug/2019:20:53:30.267]
6 frontend_name public
7 backend_name '/' server_name be_edge_http:mynamespace:test-app-service....
8 TR '/' Tw '/' Tc '/' Tr '/' Ta* 1/0/0/321/321
9 status_code 200
10 bytes_read* 135
11 captured_request_cookie -
12 captured_response_cookie -
13 termination_state --NI
14 actconn '/' feconn '/' beconn '/' srv_conn '/' retries* 1/1/1/1/0
15 srv_queue '/' backend_queue 0/0
16 '"' http_request '"' "GET /test/slowresponse/1 HTTP/1.1"
- Tq: total time in milliseconds spent waiting for the client to send a full HTTP request, not counting data
- Tw: total time in milliseconds spent waiting in the various queues
- Tc: total time in milliseconds spent waiting for the connection to establish to the final server, including retries
- Tr: total time in milliseconds spent waiting for the server to send a full HTTP response, not counting data
- Tt: total time in milliseconds elapsed between the accept and the last close. It covers all possible processings
- actconn: total number of concurrent connections on the process when the session was logged
- feconn: total number of concurrent connections on the frontend when the session was logged
- beconn: total number of concurrent connections handled by the backend when the session was logged
- srv conn: total number of concurrent connections still active on the server when the session was logged
- retries: number of connection retries experienced by this session when trying to connect to the server
Full specification: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics/blob/master/ha-proxy-log-structure.pdf
introduction of grok-exporter
Grok-exporter is a tool that can process logs based on regular expressions and convert them to one of the 4 basic Prometheus metrics:
- gauge
- counter
- histogram
- kvantilis
Grok-exporter is based on logstash-grok,and grok-exporter is using patterns and functions defined for logstash.
Detailed documentation:
https://github.com/fstab/grok_exporter/blob/master/CONFIG.md
The grok-exporter can read form three types of input sources:
- file: we will stick to this
- webhook: This solution could also be used with logstash used as rsyslog server. Logstash can send the logs to the grok-exporter webhook with the logstash plugin "http-output"
- stdin: With rsyslog, stdin can also be used. This requires the use of the omprog program, that can read data from sockets and pass on data through stdin: https://www.rsyslog.com/doc/v8-stable/configuration/modules/omprog.html
Alternative Solutions
Fluentd
To achieve the same goal with fluentd, we would need three fluentd plugins:
- fluent-plugin-rewrite-tag-filter
- fluent-plugin-prometheus
- fluent-plugin-record-modifier.
mtail:
The other alternative solution would be google's mtail, which is said to be more efficient in processing logs than the grok engine.
https://github.com/google/mtail
Configuration file
The configuration of grok-exporter can be found in /etc/grok_exporter/config.yml. There are 5 sections.
- global:
- input: Tells you where and how to retrieve logs. Can be stdin, file and webhook. We will use file input.
- grok: Location of the grok patterns. Pattern definition are stored in /grok/patterns folder by default.
- metrics: This is the most important part. Here you need to define the metrics and the associated regular expression
- server: Contains the port of the http metrics server.
Metrics
Metrics must be defined by metric types. The four basic types of Prometheus metrics are supported: Gauge, Counter, Histogram, Summary (quantile)
Each definition contains 4 parts:
- name: This will be the name of the metric
- help: This is the help text for the metric.
- match: Describes the structure of the log string in a regular expression style format. Here you can use pre-defined grok patterns:
- label: Here we can add Prometheus labels to the metrics.
match definition
Grok assumes that each element is separated by a single space in the source log files. In the match section, you have to write a regular expression using grok building blocks. Each building block has the format: %{PATTERN_NAME} where PATTERN_NAME must be an existing predefined grok pattern. The most common type is %{DATA}, which refers to an arbitrary data structure that contains no withe-space. There are several compound patterns that are build up from basic grok patterns. We can assign the regular expression result groups to named variables that can be used as the value of the Prometheus metric or as label values. The variable name must be placed inside the curly bracket of the pattern separated by a semicolon from the patter name:
%{DATA:this_is_the_name}
The result of the regular expression will be assigned to the variable this_is_the_name, which can be referenced when defining the value of the Prometheus metric or the metrics label.
labels definition
In the label section we can define labels for the generated Prometheus metric. The labels are defined with a name:value list, where the value can be a string constant or a variable defined for a pattern in the match section. The variable must be referenced in go-template style between double curly brackets starting with a dot. For example, if we used the %{DATA: this_is_the_name} pattern in the match section, we can define the 'mylabel' Prometheus label with the value of the 'this_is_the_name' variable in the following way:
mylabel: '{{.this_is_the_name}}'
Lets assume that the 'this_is_the_name' variables value is 'myvalue'. Then the metric would receive the following label: {mylabel = "myvalue"}
We are going to demonstrate a full, metric definition example in the following section
The following log line is given:
7/30/2016 2:37:03 PM adam 1.5
And there is given the following metric definition in the grok config:
metrics:
- type: counter
name: grok_example_lines_total
help: Example counter metric with labels.
match: '%{DATE} %{TIME} %{USER:user} %{NUMBER}'
labels:
user: '{{.user}}'
Here is the finale metric provided by the grok-exporter metrics endpoint:
# HELP Example counter metric with labels.
# TYPE grok_example_lines_total counter
grok_example_lines_total{user="adam"} 1
Value of the metric
For a counter-type metric, we don't need to determine the value of the metric, as it will just simply count the number of matches of the regular expression. In contrast, for all other types, we have to specify the value. It has be defined in the value section of the metric definition. Variables can be referenced in the same way as we saw it in in the label definition chapter, in go-template style. Here is an example. The following two log lines are given:
7/30/2016 2:37:03 PM adam 1 7/30/2016 2:37:03 PM Adam 5
And we define the following histogram, which consists of two buckets, bucket 1 and 2:
metrics:
- type: histogram
name: grok_example_lines
help: Example counter metric with labels.
match: '%{DATE} %{TIME} %{USER:user} %{NUMBER:val}'
buckets: [1,2]
value: '{{.val}}'
labels:
user: '{{.user}}'
This will result in the following metrics:
# HELP Example counter metric with labels.
# TYPE grok_example_lines histogram
grok_example_lines_bucket{user="adam", le="1"} 1
grok_example_lines_bucket{user="adam", le="2"} 1
grok_example_lines_bucket{user="adam", le="+Inf"} 2
grok_example_lines_count{user="adam"} 2
grok_example_lines_sum
Functions
Functions were introduced in grok-exporter version 0.2.7. We can apply functions to metric value and to the value of its labels. String manipulation functions and arithmetic functions are also available. The following two arguments arithmetic functions are supported:
- add
- subtract
- multiply
- divide
{{FUNCTION_NAME ATTR1 ATTR2}} where ATTR1 and ATTR2 can be either a natural number or a variable name. The variable name must start with a dot. Here is an example using the multiply function on the the 'grok_example_lines' metric definition form the example above:
value: "{{multiply .val 1000}}"The outcome would be:
# HELP Example counter metric with labels.
# TYPE grok_example_lines histogram
grok_example_lines_bucket {user = "adam", le = "1"} 0
grok_example_lines_bucket {user = "adam", le = "2"} 0
grok_example_lines_bucket {user = "adam", le = "+ Inf"} 2
...
Since the two values would change to 1000 and 5000, both will fall into the infinite bucket.
Creating the grok config file
We have to compile a grok pattern that can extract all the attributes that are required for creating the response-latency-histogram based on the HAproxy access-logs. The required attributes are the following:
- response time
- haproxy instance id
- openshfit service namespace
- pod name
Example haproxy access-log:
Aug 6 20:53:30 192.168.122.223 haproxy [39]: 192.168.42.1:50708 [06 / Aug / 2019: 20: 53: 30.267] public be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service / pod: test-app- 57574c8466-qbtg8: test-app-service: 172.17.0.12: 8080 1/0/0/321/321 200 135 - - --NI 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / test / slowresponse / 1 HTTP / 1.1 "
In the config.yml file, we will define a classic response-time-latency histogram, that usually contains the following buckets (in seconds):
[0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 1, 3, 8, 20, 60, 120]
Response time histogram metrics by convention are called: <name prefix>_http_request_duration_seconds
config.yml
global:
config_version: 2
input:
type: file
path: /var/log/messages
readall: true
grok:
patterns_dir: ./patterns
metrics:
- type: histogram
name: haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds
help: The request durations of the applications running in openshift that have route defined.
match: '%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:timestamp} %{DATA:Aloha_name} %{DATA:haproxy_process}: %{DATA:client_ip}:%{INT:client_port} \[%{HAPROXYDATE:accept_date}\] %{DATA:frontend_name} %{DATA}:%{DATA:namespace}:%{DATA:service}/pod:%{DATA:pod_name}:%{DATA} %{INT:Tq}/%{INT:Tw}/%{INT:Tc}/%{INT:Tr}/%{INT:Tt} %{INT:http_status_code} %{NOTSPACE:bytes_read} %{DATA} %{DATA} %{DATA} %{INT:actconn}/%{INT:feconn}/%{INT:beconn}/%{INT:srvconn}/%{NOTSPACE:retries} %{INT:srv_queue}/%{INT:backend_queue} "%{WORD:Method} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:http_version}"'
value: "{{divide .Tr 1000}}"
buckets: [0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 1, 3, 8, 20, 60, 120]
labels:
haproxy: '{{.haproxy_process}}'
namespace: '{{.namespace}}'
service: '{{.service}}'
pod_name: '{{.pod_name}}'
server:
port: 9144
Explanation:
- type:file -> read logs from file
- path: /var/log/messages -> The rsyslog server writes logs to /var/log/messages by default
- readall: true -> always reads the entire log file. This should only be used for testing, in a live environment, this always has to be set to false.
- patterns_dir: ./patterns -> Base directory of the pattern definitions in the docker image
-
value: "{{divide .Tt 1000}}"The response time in the HAproxy log is in milliseconds so we convert it to seconds. - port: 9144 -> The http port of the /metrics endpoint
Warning
Do not forget to set the value of readall to 'false' in a live environment as it can significantly degrade performance
Online grok testers
There are several online grok testing tools. These can be help to compile the required grok expression very effectively. Try this: https://grokdebug.herokuapp.com/
building the docker image
The grok-exporter docker image is available on the docker hub in several variants. The only problem with them is that they do not include the rsyslog server, what we need for the HAproxy to send logs directly to the grok-exporter pod.
docker-hub link: https://hub.docker.com/r/palobo/grok_exporter
The second problem is that they are all based on ubuntu image, that makes it very difficult to get rsyslog to log to stdout (ubunto doesn't support loggin to stdout), which required by the centralized log system. We are going to port the original grok Dockerfile to centos 7 base image and will add rsyslog installation to the new image.
All necessary files are available under my git-hub: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics/tree/master/grok-exporter-centos
I also created an ubuntu based solution, which is an extension of the original docker-hub version, which can also be found on git-hub in the grok-exporter-ubuntu folder. In the rest of this chapter, we are going to use the centOS version.
Dockerfile
We will modify the official palobo/grok_exporter Dockerfile, we will extend it with the rsyslog installation and port it to centos: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics/tree/master/grok- CentOS-exporter
➲File:Grok-exporter-docker-build.zip
Dockerfile
FROM centos:7
LABEL Maintainer="Adam Berki <https://github.com/berkiadam/>"
LABEL Name="grok_exporter"
LABEL Version="0.2.8"
ENV PID_DIR /tmp/pidDir
ENV GROK_ARCH="grok_exporter-0.2.8.linux-amd64"
ENV GROK_VERSION="v0.2.8"
USER root
RUN yum -y install rsyslog wget unzip && \
yum clean all && \
echo "" > /etc/rsyslog.d/listen.conf && \
mkdir -p ${PID_DIR} && \
chmod 777 ${PID_DIR} \
&& wget https://github.com/fstab/grok_exporter/releases/download/$GROK_VERSION/$GROK_ARCH.zip \
&& unzip $GROK_ARCH.zip \
&& mv $GROK_ARCH /grok \
&& rm $GROK_ARCH.zip \
&& yum -y remove wget unzip \
&& rm -fr /var/lib/apt/lists/*
RUN mkdir -p /etc/grok_exporter && ln -sf /etc/grok_exporter/config.yml /grok/
COPY rsyslog.conf /etc/rsyslog.conf
EXPOSE 514/tcp 514/udp 9144/tcp
WORKDIR /grok
CMD sh -c "nohup /usr/sbin/rsyslogd -i ${PID_DIR}/pid -n &" && ./grok_exporter -config /grok/config.yml
Note
It is important to use grok-exporter version 0.2.7 or higher, as functions were introduced in this version
The rsyslog.conf file include at least the following, that enables receiving logs on port 514 over both UDP and TCP (see zip above for details). The logs are written to stdout and to /var/log/messages.
$ModLoad omstdout.so # provides UDP syslog reception module(load="imudp") input(type="imudp" port="514") # provides TCP syslog reception module(load="imtcp") input(type="imtcp" port="514") ... *.* :omstdout: # send everything to stdout *.*;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
Local build and local test
First, we will build the docker image with the local docker daemon so that we can run it locally for testing. Later we will build it directly on the minishfit VM, since we will only be able to upload it to the minishfit docker registry from the VM. Since, at the and, as we will upload the image to a remote docker repository, it is important to follow the naming conventions:
<repo URL>: <repo port> / <namespace> / <image-name>: <tag>
We will upload the image to the docker registry running on the minishift, so it is important to specify the address and port of the minishfit-docker registry and the OpenShift namespace where the image will be deployed.
# docker build -t 172.30.1.1:5000/default/grok_exporter:1.1.0.
The image can be easily tested locally. Create a haproxy test log file (haproxy.log) with the following content in it. This will be processed by the grok-exporter during the test, as if it had been provided by haproxy.
Aug 6 20:53:30 192.168.122.223 haproxy[39]: 192.168.42.1:50708 [06/Aug/2019:20:53:30.267] public be_edge_http:mynamespace:test-app-service/pod:test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8:test-app-service:172.17.0.12:8080 1/0/0/321/321 200 135 - - --NI 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET /test/slowresponse/1 HTTP/1.1" Aug 6 20:53:30 192.168.122.223 haproxy[39]: 192.168.42.1:50708 [06/Aug/2019:20:53:30.588] public be_edge_http:mynamespace:test-app-service/pod:test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8:test-app-service:172.17.0.12:8080 53/0/0/11/63 404 539 - - --VN 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1"
Put the grok config file config.yml specified above in the same folder. In the config.yml file, change the input.path to /grok/haproxy.log where the test log content is. Then start the container with following docker run' 'command:
# docker run -d -p 9144: 9144 -p 514: 514 -v $ (pwd) /config.yml:/etc/grok_exporter/config.yml -v $ (pwd) /haproxy.log:/grok/haproxy. log --name grok 172.30.1.1:5000/default/grok_exporter:1.1.0
Check the logs and confirm that the grok and rsyslog both have started:
# docker logs grok * Starting enhanced syslogd rsyslogd ... done. Starting server is http: // 7854f3a9fe76: 9144 / metrics
Metrics are available in the browser at http://localhost:9144/metrics:
...
# HELP haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket The request duration of the applications running in openshift that have route defined.
# TYPE haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket histogram
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="0.1"} 1
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="0.2"} 1
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="0.4"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="1"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="3"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="8"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="20"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="60"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="120"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service",le="+Inf"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket_sum{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service"} 0.384
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket_count{haproxy="haproxy[39]",namespace="mynamespace",pod_name="test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8",service="test-app-service"} 2
As a second step, verify that the rsyslog' 'running in the docker container can receive remote log messages. To do this, first enter the container with the exec command and check the content of the /var/log/messages file in f (follow) mode.
# docker exec -it grok /bin/bash root@a27e5b5f2de7:/grok# tail -f /var/log/messages Aug 8 14:44:37 a27e5b5f2de7 rsyslogd: [origin software="rsyslogd" swVersion="8.16.0" x-pid="21" x-info="http://www.rsyslog.com"] start Aug 8 14:44:37 a27e5b5f2de7 rsyslogd-2039: Could not open output pipe '/dev/xconsole':: Permission denied [v8.16.0 try http://www.rsyslog.com/e/2039 ] Aug 8 14:44:37 a27e5b5f2de7 rsyslogd: rsyslogd's groupid changed to 107 Aug 8 14:44:37 a27e5b5f2de7 rsyslogd: rsyslogd's userid changed to 105 Aug 8 14:44:38 a27e5b5f2de7 rsyslogd-2007: action 'action 9' suspended, next retry is Thu Aug 8 14:45:08 2019 [v8.16.0 try http://www.rsyslog.com/e/2007 ]
Now, on the host machine, use the logger command to send a log message to the container running rsyslog server on port 514:
# logger -n localhost -P 514 -T "this is the message"
(T = TCP)
The log should then appear in the syslog' 'file:
Aug 8 16:54:25 dell adam this is the message
You can delete the local docker container.
Remote build
We have to to upload our custom grok Docker image to the minishfit registry. To do so, you need to build the image with the minishfit VM's local docker daemon, since you can only access the minishfit registry from the VM so uploading images is only possible from the VMs local registry.
Details can be found here: ➲Image push to minishift docker registriy
We need special rights for accessing the minishift registry even from the VM running the minishfit cluster. In the example we always log in to minishfit as admin user, so we are going to extend the admin user with the cluster-admin role, that has sufficient rights for uploading images to the minishift registry. For extending our user roles we have to log into the system namespace, so always include the namespace name in the 'oc login' command.
# oc login -u system:admin # oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin admin --as = system: admin cluster role "cluster-admin" added: "admin"
Note
If we get this error Error from server (NotFound): the server could not find the requested resource, it probably means that our oc client is older than OpenShift version
Redirect our local docker client to the docker daemon running on the minisfhit VM and log into the minishift docker registry:
# minishift docker-env # eval $ (minishift docker-env) # oc login Username: admin Password: <admin> # docker login -u admin -p $ (oc whoami -t) $ (minishift openshift registry) Login Succeeded
Build the image on the minishfit VM as well:
# docker build -t 172.30.1.1:5000/default/grok_exporter:1.1.0.
Push the image to the minisfhit registry:
# docker push 172.30.1.1:5000/default/grok_exporter:1.1.0
Required Kubernetes objects
For the HAproxy-exporter we will create a serviceAccount, a deployment, a service and a comifMap where we will store the grok-exporter configuration. In addition, we will extend the anyuid SecurityContextConstraints object, because the rsyslog server requires the grok-exporter container to run in privileged mode.
- haproxy-exporter service account
- cm-haproxy-exporter.yaml
- deployment-haproxy-exporter.yaml
- svc-haproxy-exporter-service.yaml
- scc-anyuid.yaml
The full configuration can be downloaded here: File:Haproxy-kubernetes-objects.zip or can be found in the git repository below: https://github.com/berkiadam/haproxy-metrics
Create the ServiceAccount
# kubectl create serviceaccount haproxy-exporter -n default serviceaccount / haproxy-exporter created
As a result, the following serviceAccount definition was created:
apiVersion: v1
imagePullSecrets:
- name: haproxy-exporter-dockercfg-67x4j
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: haproxy-exporter
namespace: default
secrets:
- name: haproxy-exporter-token-8svkx
- name: haproxy-exporter-dockercfg-67x4j
Addition Kubernetes objects
cm-haproxy-exporter.yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
config.yml: |
...grok-exporter config.yml...
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: haproxy-exporter
namespace: default
deployment-haproxy-exporter.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
...
name: haproxy-exporter
namespace: default
spec:
...
template:
...
spec:
containers:
- image: '172.30.1.1:5000/default/grok_exporter:1.1.0'
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: grok-exporter
ports:
- containerPort: 9144
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 514
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/grok_exporter/
name: config-volume
- mountPath: /var/log
name: log-dir
...
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: haproxy-exporter
- name: log-dir
emptyDir: {}
svc-haproxy-exporter-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
run: haproxy-exporter
name: haproxy-exporter-service
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- name: port-1
port: 9144
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9144
- name: port-2
port: 514
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 514
- name: port-3
port: 514
protocol: UDP
targetPort: 514
selector:
run: haproxy-exporter
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
SecurityContextConstraints
Because of Haproxy-exporter runs an rsyslog server, its container must be run in privileged mode. To do this, you need to add the HAproxy-exporter serviceAcccount to the SCC named anyuid'. So we don't need the privileged SCC because the container wants to start as root, we don't need to force it by OpenShift configuration, we just have to allow it. Without running as root, rsyslog will not be able to create sockets.
Lets list the SCCs:
# kubectl get SecurityContextConstraints NAME PRIV CAPS SELINUX RUNASUSER FSGROUP SUPGROUP PRIORITY READONLYROOTFS VOLUMES anyuid false [] MustRunAs RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny 10 false [configMap downwardAPI emptyDir persistentVolumeClaim ... privileged true [*] RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny RunAsAny <none> false [*] ...
The haproxy-exporter service-account must be added to the users section of the 'anyuid' SCC in the following format:
- system: serviceaccount: <namespace>: <serviceAccount>
Scc-anyuid.yaml
kind: SecurityContextConstraints
metadata:
name: anyuid
...
users:
- system: serviceaccount: default: haproxy-exporter
...
Since this is an existing scc and we just want to apply some minor changes, we can edit it 'on the fly' with the 'oc edit' command:
# oc edit scc anyuid securitycontextconstraints.security.openshift.io/anyuid edited
create the objects
# kubectl apply -f cm-haproxy-exporter.yaml configmap / haproxy-exporter created
# kubectl apply -f deployment-haproxy-exporter.yaml deployment.apps / haproxy-exporter created # kubectl rollout status deployment haproxy-exporter -n default deployment haproxy-exporter successfully rolled out
# kubectl apply -f svc-haproxy-exporter-service.yaml
Testing
Find the haproxy-exporter pod and check logs of the pod:
# kubectl logs haproxy-exporter-744d84f5df-9fj9m -n default * Starting enhanced syslogd rsyslogd ... done. Starting server on http: // haproxy-exporter-744d84f5df-9fj9m: 9144 / metrics
Then enter the container and test the rsyslog server:
# kubectl exec -it haproxy-exporter-647d7dfcdf-gbgrg / bin / bash -n default
Then use the logger command to send a log message to rsyslog.
logger -n localhost -P 514 -T "this is the message"
Now, let's list the contents of the /var/log/messages folder:
# cat messages Aug 28 19:16:09 localhost root: this is the message
Exit the container and retrieve the pod logs again to see if the log has been sent to stdout as well:
# kubectl logs haproxy-exporter-647d7dfcdf-gbgrg -n default Starting server on http: // haproxy-exporter-647d7dfcdf-gbgrg: 9144 / metrics 2019-08-28T19: 16: 09 + 00: 00 localhost root: this is the message
HAproxy Configuration
Setting the environment variables
In the HAproxy routers, we will set the address of the rsyslog server running in the haporxy-exporter pod via environment variables. Let's check first the haproxy-exporter service.
# kubectl get svc -n default NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT (S) AGE haproxy-exporter-service ClusterIP 172.30.213.183 <none> 9144 / TCP, 514 / TCP, 514 / UDP 15s ..
HAproxy stores the rsyslog server address in the ROUTER_SYSLOG_ADDRESS environment variable. We can overwrite this at runtime with the oc set env command. After rewriting the variable, the pod will restart automatically.
# oc set env dc / myrouter ROUTER_SYSLOG_ADDRESS = 172.30.213.183 -n default deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated
Note
In minishift, in the router containers the name resolution does not work for Kubernetes service names, because it doesn't use the Kubernetes cluster DNS server but the minishfit VM. Therefore, all you have to do is enter the service's IP address instead of its name. In OpenShift, we have to use the name of the service
As a second step, change the HAproxy log level to debug, because it only produces access log in debug level.
# oc set env dc / myrouter ROUTER_LOG_LEVEL = debug -n default deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated
Warning
Performance test must be carried out to see how much is the extra load when running the haproxy in debug mode
As a result of the modification of the two environment variables, the configuration of HAproxy in /var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config has changed to:
# kubectl exec -it myrouter-5-hf5cs / bin / bash -n default $ cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config global .. log 172.30.82.232 local1 debug
This is the IP address of the haproxy-exporter service, and the log level is debug.
Testing the rsyslog server
Generate some traffic through haproxy, then go back to the haproxy-exporter container and list the content of the messages file.
# kubectl exec -it haproxy-exporter-744d84f5df-9fj9m/bin/bash -n default # # tail -f /var/log/messages Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy fe_sni stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_no_sni stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy fe_no_sni stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy openshift_default stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 1 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_edge_http: dsp: nginx-route stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_http: mynamespace: prometheus-alertmanager-jv69s stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_http: mynamespace: prometheus-server-2z6zc stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [24]: Proxy be_edge_http: myproject: nginx-route stopped (FE: 0 conns, BE: 0 conns). Aug 9 12:52:17 192.168.122.223 haproxy [32]: 127.0.0.1:43720 [09 / Aug / 2019: 12: 52: 17.361] public openshift_default / <NOSRV> 1 / -1 / -1 / -1 / 0 503 3278 - - SC-- 1/1/0/0/0 0/0 "HEAD / HTTP / 1.1"
http://test-app-service-mynamespace.192.168.42.185.nip.io/test/slowresponse/3000
... Aug 9 12:57:21 192.168.122.223 haproxy [32]: 192.168.42.1:48266 [09 / Aug / 2019: 12: 57: 20.636] public be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service / pod: test-app- 57574c8466-qbtg8: test-app-service: 172.17.0.17: 8080 1/0/12/428/440 200 135 - - --II 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / test / slowresponse / 1 HTTP / 1.1 " Aug 9 12:57:28 192.168.122.223 haproxy [32]: 192.168.42.1:48266 [09 / Aug / 2019: 12: 57: 21.075] public be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service / pod: test-app- 57574c8466-qbtg8: test-app-service: 172.17.0.17: 8080 4334/0/0/3021/7354 200 135 - - --VN 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / test / slowresponse / 3000 HTTP / 1.1 " Aug 9 12:57:28 192.168.122.223 haproxy [32]: 192.168.42.1:48266 [09 / Aug / 2019: 12: 57: 28.430] public be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service / pod: test-app- 57574c8466-qbtg8: test-app-service: 172.17.0.17: 8080 90/0/0/100/189 404 539 - - --VN 2/2/0/1/0 0/0 "GET /favicon.ico HTTP /1.1 " Aug 9 12:57:35 192.168.122.223 haproxy [32]: 192.168.42.1:48268 [09 / Aug / 2019: 12: 57: 20.648] public public / <NOSRV> -1 / -1 / -1 / -1 / 15002 408 212 - - cR-- 2/2/0/0/0 0/0 "<BADREQ>"
Testing the grok-exporter component
Please open the gork-exporter metrics at http://<pod IP>:9144/metrics. You can open this URL either in the haproxy-exporter pod itself with on localhost or in any other pod using the haporxy-exporter pod's IP address. We have to see the haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket histogram among the metrics.
# kubectl exec -it test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8/bin/bash -n mynamespace
$
$ curl http://172.30.213.183:9144/metrics
...
# HELP haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds The request durations for the applications running in openhift that have route defined.
# TYPE haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds histogram
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "0.1"} 0
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "0.2"} 1
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "0.4"} 1
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "1"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "3"} 2
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "8"} 3
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "20"} 3
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "60"} 3
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "120"} 3
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket haproxy = { "haproxy [32]" namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service", le = "+ Inf"} 3
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_sum {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service"} 7.9830000000000005
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_count {haproxy = "haproxy [32]", namespace = "mynamespace", pod_name = "test-app-57574c8466-qbtg8", service = "test-app-service"} 3
Prometheus Settings
Static configuration
- job_name: grok-exporter
scrape_interval: 5s
metrics_path: / metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ['grok-exporter-service.default: 9144']Pod Level Data Collection
We want the haproxy-exporter pods to be scalable. This requires that the Prometheus does not scrape the metrics through the service (because it does loadbalancing), but from the pods directly. So Prometheus must query the Endpoint definition assigned to the haproxy-exporter service from the Kubernetes API, which contains the list of IP addresses the pods. We will use the 'kubernetes_sd_configs element to achieve his. (This requires Prometheus to be able to communicate with the Kubernetes API. For details, see Prometheus_on_Kubernetes)
When using kubernetes_sd_configs Prometheus always gets a list of a specific Kubernetes objects from the API (node, service, endpoints, pod) and then it identifies those resources according to its configuration from which it wants to collect the metrics. In the ''relabel_configs section of Prometheus configuration we will define filter conditions for identifying the needed resources. In this case, we want to find the endpoint belonging to the haproxy-exporter service, because it allows Prometheus to find all the pods for the service. So, based on Kubernetes labels, we want to find the endpoint that is called ' 'haproxy-exporter-service and has a port called metrics through which Prometheus can scrape the metrics. In Prometheus, the default scrape URL is /metrics, so we don't have to define it implicitly.
# kubectl get Endpoints haproxy-exporter-service -n default -o yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Endpoints metadata: name: haproxy-exporter-service ... ports: - name: log-udp port: 514 protocol: UDP - name: metrics port: 9144 protocol: TCP - name: log-tcp port: 514 protocol: TCP
We are looking for two labels in the Endpoints list:
- __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name: metrics -> 9144
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name: haproxy-exporter-service
The config-map that describes proetheus.yaml, should be extended with the following:
<source lang = "C ++">
- job_name: haproxy-exporter
scheme: http
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
server_name: router.default.svc
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
namespaces:
names:
- default
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name]
action: keep
regex: haproxy-exporter-service; metrics
</ Source>
Reload configMap:
# kubectl apply -f cm-prometheus-server-haproxy-full.yaml
Wait for Prometheus to read the configuration file again:
# kubectl logs -f -c prometheus-server prometheus-server-75c9d576c9-gjlcr -n mynamespace ... level = info ts = 2019-07-22T20: 25: 36.016Z caller = main.go: 730 msg = "Loading configuration file" filename = / etc / config / prometheus.yml
Then, on the http://mon.192.168.42.185.nip.io/targets screen, verify that Prometheus can scrape the haproxy-exporter target:
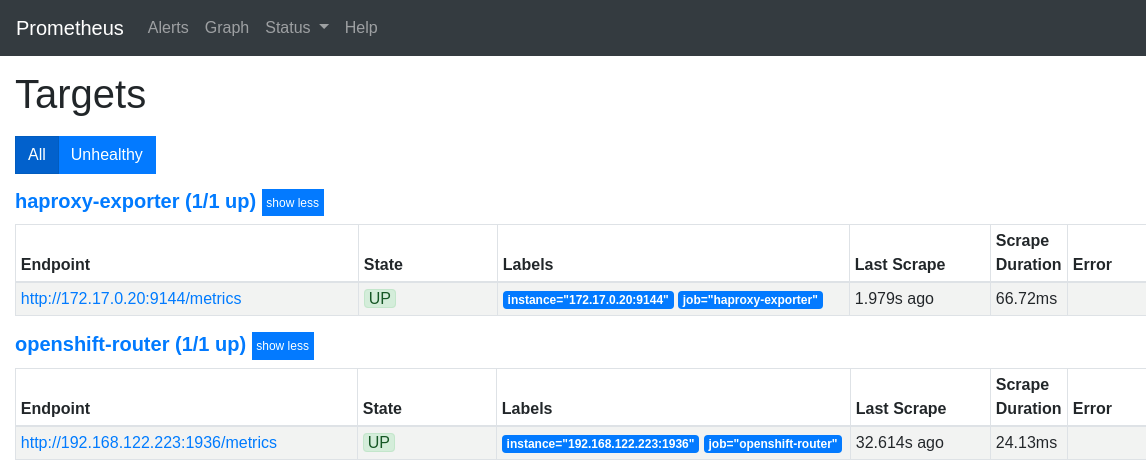
scaling haproxy-exporter
# kubectl scale deployment haproxy-exporter --replicas = 2 -n default deployment.extensions / haproxy-exporter scaled
# kubectl get deployment haproxy-exporter -n default NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE haproxy-exporter 2 2 2 2 3h
Metric types
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket
type: histogram
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_bucket_count
type: counter
The total number of requests in that histogram
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_count haproxy = { "haproxy [39]", Job = "haproxy-exporter" namespace = "mynamespace" pod_name = "app-body" service = "body-app-service"} 5
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_sum
type: counter
The sum of the response times in a given histogram. Based on the previous example, there were a total of 5 requests and the summ serving time was 13 s.
haproxy_http_request_duration_seconds_sum haproxy = { "haproxy [39]", Job = "haproxy-exporter" namespace = "mynamespace" pod_name = "app-body" service = "body-app-service" 13663}
OpenShift router + rsyslog
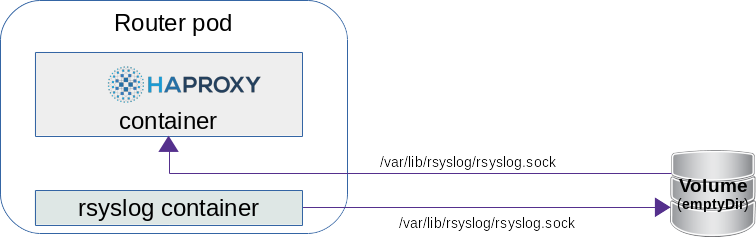
Starting with OpenShift 3.11, it is possible to fire up a router that will contain a side car rsyslog container in the router pod and configure HAproxy to send logs to the rsyslog server via an emptyDir volume , which writes them to stdout by default. The configuration of rsyslog is in a configMap.
You can create a router with syslogserver using the --extended-logging switch in the ' 'oc adm router command.
# oc adm router myrouter --extended-logging -n default info: password for stats user admin has been set to O6S6Ao3wTX -> Creating router myrouter ... configmap "rsyslog-config" created warning: serviceaccounts "router" already exists clusterrolebinding.authorization.openshift.io "router-myrouter-role" created deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io "myrouter" created service "myrouter" created -> Success
Turn on debug level loging in HAproxy:
# oc set env dc / myrouter ROUTER_LOG_LEVEL = debug -n default deploymentconfig.apps.openshift.io/myrouter updated
There are two containers in the new router pod:
# kubectl describe pod / myrouter-2-bps5v -n default .. Containers: router: Image: openshift / origin-haproxy-router: v3.11.0 Mounts: / var / lib / rsyslog from rsyslog-socket (rw) ... syslog: Image: openshift / origin-haproxy-router: v3.11.0 Mounts: / etc / rsyslog from rsyslog-config (rw) / var / lib / rsyslog from rsyslog-socket (rw) ... rsyslog-config: Type: ConfigMap (a volume populated by a ConfigMap) Name: rsyslog-config Optional: false rsyslog-socket: Type: EmptyDir (a temporary directory that shares a pod's lifetime) Medium: SizeLimit: <unset>
You can see that the /var/lib/rsyslog/ folder is mounted in both containers. The rsyslog.sock file will be created here.
router container
When we enter the router container, we can see that the configuration has already been modified:
# kubectl exec -it myrouter-2-bps5v / bin / bash -n default -c router bash-4.2 $ cat /var/lib/haproxy/conf/haproxy.config global ... log /var/lib/rsyslog/rsyslog.sock local1 debug ... defaults ... option httplog -> Enable logging of HTTP request, session state and timers ... backend be_edge_http: mynamespace: test-app-service
rsyslog container
# kubectl exec -it myrouter-2-bps5v / bin / bash -n default -c syslog $ cat /etc/rsyslog/rsyslog.conf $ ModLoad imuxsock $ SystemLogSocketName /var/lib/rsyslog/rsyslog.sock $ ModLoad omstdout.so *. *: omstdout:
If you want to reconfigure rsyslog to send logs to e.g, logstash then you only need to rewrite the configMap. By default, rsyslog only writes to stdout.
# kubectl get cm rsyslog-config -n default -o yaml apiVersion: v1 data: rsyslog.conf: | $ ModLoad imuxsock $ SystemLogSocketName /var/lib/rsyslog/rsyslog.sock $ ModLoad omstdout.so *. *: omstdout: kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rsyslog-config namespace: default
Viewing HAproxy Logs
# kubectl logs -f myrouter-2-bps5v -c syslog