KVM
Contents
Introduction
hypervisor
A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) is computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources
- Type 1 hypervisor: hypervisors run directly on the system hardware – A “bare metal” embedded hypervisor,
- Type 2 hypervisor: hypervisors run on a host operating system that provides virtualization services, such as I/O device support and memory management.
KVM
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a virtualization infrastructure for the Linux kernel that turns it into a hypervisor. It was merged into the Linux kernel mainline in kernel version 2.6.20, which was released on February 5, 2007.KVM requires a processor with hardware virtualization extensions.
libvirt
libvirt is an open-source API, daemon and management tool for managing platform virtualization.[3] It can be used to manage KVM, Xen, VMware ESX, QEMU and other virtualization technologies. These APIs are widely used in the orchestration layer of hypervisors in the development of a cloud-based solution.
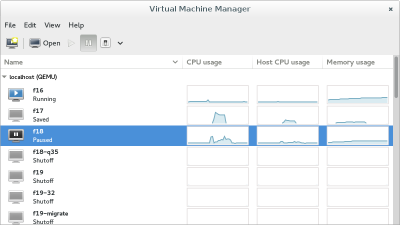
Virtual Machine Manager (app)
The virt-manager application is a desktop user interface for managing virtual machines through libvirt. It primarily targets KVM VMs, but also manages Xen and LXC (linux containers). It presents a summary view of running domains, their live performance & resource utilization statistics. Wizards enable the creation of new domains, and configuration & adjustment of a domain’s resource allocation & virtual hardware. An embedded VNC and SPICE client viewer presents a full graphical console to the guest domain.
Manage KVM
Manage networks
List all
# virsh net-list Name State Autostart Persistent ---------------------------------------------------------- default active yes yes docker-machines active yes yes
# virsh net-info default Name: default UUID: 3eb5cb82-b9ea-4a6e-8e54-1efea603f90c Active: yes Persistent: yes Autostart: yes Bridge: virbr0 <pre>Start networks
<pre>
<pre>
- virsh net-autostart default
- virsh net-start default